World Climate Map
Day One
- Study World Weather Maps:
http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/climate.html ( biomes)
http://www.climate-charts.com/World-Climate-Maps.html ( maps of climates)
http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es2103/es2103page01.cfm?chapter_no=21 ( cool interactive)
http://www.climate-zone.com/ ( interactive)
The Weather Book by Michael Oard
Day Two
- Color in the climate zones on the world map. Use a different color for each zone.
- Define the 8 zones
Polar and Tundra
Cold Forest
Temperate
Mountain
Deserts
Dry Grassland
Tropical Grasslands
Rain Forest
- Define the three basic climate groups.
Low Latitude Climates
Mid Latitude Climates
High Latitude Climates
Day Three
- How does climate affect our food supply? ( activity)http://extension.usu.edu/aitc/teachers/pdf/lesson/winter00_agzone.pdf ( lesson plans on food and climate)
- How do we use maps and climate to plan our gardening? ( activity)
http://www.tulipworld.com/hardinesszipzone.asp US planting zones
http://www.raintreenursery.com/map_usdaHardiness.html US planting zones
- What is Latitude and Longitude? ( Review for my kids so a short lesson. You may want to spend more time here and do maps etc)
http://nationalatlas.gov/articles/mapping/a_latlong.html
http://www.worldatlas.com/aatlas/imageg.htm interactive
http://itouchmap.com/latlong.html interactive
Day Four
Sun Rays
- Activity 1 ( pencils) Janice Van Cleave's Weather
- Sun Rays Activity 2 (cardboard) Weather and Climate, Barbara Taylor
Earth not tilted Earth Tilted
- Sun Rays Activity 3 ( earth model) Weather and Climate. Barbara Taylor
Keep the ball spinning at a 23.5 degree angle and walk around the sun.
- Sun Rays Activity 4 using spray paint and a ball
Spray straight on with earth ( ball at a 23.5 degree )
http://www.fourmilab.ch/cgi-bin/Earth This site will enable you to see how the above activities work.
Seasons of the Year Activities

o Draw a diagram of How Seasons Work
http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/uts/seasons1.html
http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Seasons.shtml
Day Five
The Power of the Sun
Hot Air Activities
o Bubbles Activity
o Spiral Activity ( Convection) Kids love this one. The spiral moves and dances. The camera picks up convection really well.
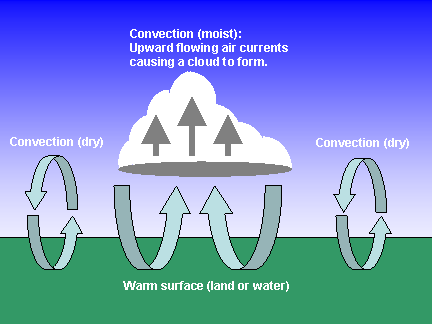
What is convection?
"Convection" has several, related meanings in weather....but it always involves rising air. It usually refers to "moist convection", where the excess water vapor in rising air parcels condenses to form a cloud. The heat released through this condensation can help to sustain the convection by warming the air further and making it rise still higher, which causes more water vapor to condense, so the process feeds on itself. Convection can also be dry, as occurs on a sunny day over the desert. The sun warms the ground, and convective air currents help to remove the excess heat from the surface. Dry convection also occurs during the day even when clouds are forming...you just can't see it.
Interesting facts:
MAKING THE EARTH LIVEABLE: Convection (both dry and moist) help to make the Earth liveable by removing excess heat from the surface, and transporting it high into the atmosphere. It has been calculated that, without convection, the average surface air temperature on the earth would be about 125 deg. F, rather than the current 59 deg. F.
Can You Cook with the Sun? ( a bit off topic)
http://www.re-energy.ca/pdf/solaroven.pdf
http://pbskids.org/zoom/activities/sci/solarcookers.html
http://www.freewebs.com/sunnycooker/suntasticcookerplan.htm
http://www.hometrainingtools.com/articles/build-a-solar-oven-project.html
Vocabulary
Just for fun try this! http://education.jlab.org/vocabhangman/index.html
Axis
A line on which an object rotates. The Earth’s axis runs
through its center from the North Pole to the South Pole.
Plane of Ecliptic
The plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. Except for
Pluto, all of the planets’ orbits lie roughly in this plane.
Revolution
The motion of one body around another.
Rotation
The spinning motion of a planet or other object on
its axis.
Solstice
Two times during the year when the sun is at its
Greatest distance from the celestial equator and
appears to be farthest north or south. Northern
Hemisphere, June 21 or 22, the summer solstice
is the longest day of the year. Dec. 21 or 22 is
the shortest day of the year, winter solstice.
Vernal, having to do with spring; vernal
equinox, about March 21.
Autumnal, having to do with autumn or fall;
autumnal equinox, about September 22.
Equinox, Two times during the year when
the center of the sun crosses the celestial
equator, and day and night are of equal
length in all parts of the earth.
Equator, an imaginary circle around the
middle of the earth, halfway between the
North Pole and the South Pole.
Perpendicular, at right angles to a given line,
plane, or surface.
Parallel, two lines that lie in the same plane
and do not intersect.
Ellipse, oval having both ends alike.
Longitude, the distance east or west on the
earth’s surface, measured in degrees from a
certain meridian, usually the Prime Meridian.
Latitude, the distance north or south of the
equator, measured in degrees. A degree of
latitude is 69.2 miles.
Day: The period of 24 hours of day and
night; time it takes for the earth to make one
rotation on its axis.
Night: The time between evening and
morning; the time from sunset to sunrise.
Year: The period of the earth’s revolution
around the sun; 12 months or 365 days (366
in leap years).






No comments:
Post a Comment